5 Terms You Must Know About Your Health Insurance
![]() March 10, 2024
March 10, 2024
![]() 0 Comments
0 Comments
Health insurance is the basic foundation of a sound financial plan. A health insurance policy can help you cover the costs of medical surgeries, expenses, and other procedures. With a comprehensive health policy in place, your overall planning can largely stay unaffected as unexpected medical bills can be covered or reimbursed by health policies. With the rising medical inflation, the cost of surgeries and procedures in India is rising. Hence, health coverage is a necessary step you should be taking toward your finances. Moreover, buying a policy isn’t sufficient if you do not give the time to understand it. Knowing the common health insurance terminology can help you get the most out of it. Here are some crucial terms you should be aware of, which are largely standardised across the industry.
Health Insurance Terminologies
PED: Pre-existing disease or PED is a declaration required to be given to the insurer before buying the policy. Insurers only cover hospitalisation costs after a waiting period if it is related to a pre-existing medical condition. This period is generally 2-4 years.
Co-pay & Sub-limits: A co-payment is a % of the bill that the policyholder is required to pay. This clause is common in cheaper policies and senior citizen plans. For instance, in a policy with a 15% co-pay, the policyholder will be required to pay for 15% of the total expense while the rest will be covered by the insurer. Sub-limit is another form of cap on the coverage amount but on specific diseases. The clause specifies the maximum an insurer is willing to pay if you go for the listed surgeries or procedures.
Room Rent Limit: This is a cap put on the type of hospital room you can choose. Hospital rooms have a daily rent. This clause restricts the policyholder from going for more plush rooms. Going with a room that exceeds the cap can reduce the amount your insurer will cover. Further, services rendered in the room, like diagnostic, surgeon fees, consultant fees, etc., will not be covered fully.
NCB: No Claim Bonus is a perk given by the insurer for a claim-free year. You can think of it as an incentive by the insurer for your good health in the past year. Usually, the basic sum insured increases by a fixed % for every claim-free year and is limited up to a certain amount. For instance, 25% for every claim-free year with a cap of 100% (of the basic sum insured). Finally, the bonus may also be reduced at the same rate at which it has accrued in case of claims.
Restoration Benefit: This benefit can restore your sum insured back to the initial amount if you have claimed some benefit. For instance, if your sum insured is 10 lakhs and you claim for a medical treatment costing 8.5 lakhs, the sum insured now reduces to 1.5 lakhs. But this will be restored to the original sum insured if you have a restoration benefit in your policy. It can help you pay your costs if you are hospitalised once more in the same year. There may be restrictions on using the restored benefit. Some policies may not let you use the benefit for the same illness once again.
Thank you for taking the time to read.
If you have a question, share it in the comments below or DM us or call us - +91 9051052222. We'll be happy to answer it.
- Nischay Avichal
Share With
I'm a cool paragraph that lives inside of an even cooler modal. Wins!
Are you sure?
In case you didnt know, you can open your account online within 24 hours. Offline account opening takes up to 4 working days. If you wish to open your account offline, fill and sign the forms using a black/blue ballpoint pen. Please fill in the email and mobile number of the applicant to avoid account opening delays.
Enter Password
Please enter your details and password
New to Dayco?
Enter Password
Please enter your details and password
New to Dayco?
Filing Complaints on SCORES (SEBI) – Easy & Quick
- Register on SCORES Portal (SEBI)
- Mandatory details for filing complaints on SCORES:
- Name, PAN, Address, Mobile Number, E-mail ID
- Benifits:
- Effective Communication
- Speedy redressal of the grievances
Thanks !!
Your details were successfully received.

Thank you for Your Feedback!
Our Team is working constantly on improving our user experience and your feedback really means a lot.
Thanks !!
App Link Send to your mobile number successfully.
Thank You
All your Questions have been recorded
Thank You
All your Questions have been recorded
Thank You!
Thank you for your response. We'll get in touch with you at the earlisest for your investment planning needs
NEXT
Thank You!
Thank You for your interest in our Moderate Equity Portfolio. Please find below the credentials to track this portfolio:
User ID: mockmod@daycoindia.com
Password: abcd@1234
Portfolio Tracker
Please Read!
Risk profiling is crucial for identifying and managing potential risks in investment decisions. Please carry out your risk profiling before making any investment decisions.
Complete Risk Assessment Now
Thank You !!
Please enter your details to download/print the report
Thank You !!
Please enter your details to download/print the report
Thank You !!
Please enter your details to download/print the report
Thank You !!
Please enter your details to download/print the report
Thank You !!
Please enter your details to download/print the report
Set Your Goal
Please Select an option from below
Set Your Goal
Please Select an option from below
Thanks You !
We appreciate your interest in our services. Our team will be in touch with you shortly.
CloseSet your Goal
Please enter your details in the fields provided
Thanks You!!
Calculation report has been sent to your mail id successfully
Clear form?
This will remove your answers from all questions and cannot be undone.



 Book Appointment
Book Appointment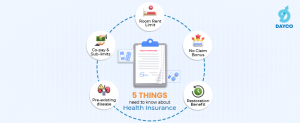









Leave a Reply